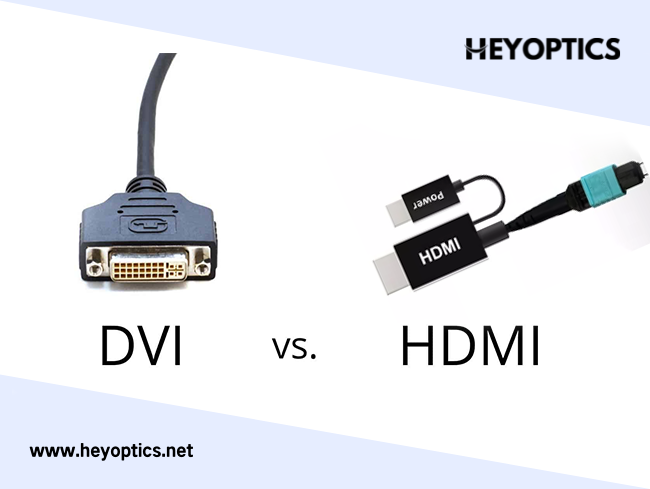
HDMI Over IP vs HDBaseT – Which to Choose?
Building a network with minimum cables has become an important requisite for businesses these days. This is because cable cluttering may result in confusion and accidents if not managed properly. Fortunately, several technologies have been developed to accomplish this. Both HDMI over IP and HDBaseT can be used to transmit high-definition video and audio.
HDMI Over IP and HDBaseT are increasingly popular and have gained immense acceptance owing to their beneficial features. Both HDMI over IP and HDBaseT distribute high-definition video signals from a single source to multiple screens using the existing Ethernet infrastructure. The distribution of video signals is performed using devices such as switches, adapters, splitters, and so on. However, both technologies do it differently. Whether to choose HDMI Over IP or HDBaseT largely depends upon your application needs.
What are their differences? Which one should we choose? Read through this post to get detailed comparisons of HDMI over IP vs HDBaseT and make an appropriate choice between them.
What is HDMI Over IP?
As discussed earlier, HDMI over IP or HDMI transmit high definition audio and video over Ethernet using devices such as switches, extenders, adapters, and Ethernet-enabled HDMI cables. These devices distribute received signals to multiple destinations without any degradation. An Ethernet HDMI cable can support a high speed of 100Mb per second required for the most demanding networking applications. HDMI over IP is best suited for long-distance data transmission. It uses fiber optic cables and AV/KVM extension devices for transmitting audio or video over long distances at a high resolution.
What is HDBaseT?
HDBaseT is a global standard used for the data transmission of uncompressed ultra-high-definition multimedia contents. The keystone of the technology is 5play that enables up to 8Gbps of high definition digital video and audio as well as control signals to be transmitted over a single cable on 100BaseT Ethernet. Since its introduction in 2010, the technology has drastically transformed the video distribution sector with increased reach, a rich feature set, and improved performance. HDBaseT provides a seamless experience by eliminating cable clutter without compromising on performance and quality.
HDMI Over IP vs HDBaseT
HDMI over IP, also known as AV over IP, HD over IP, Video over IP, HDIP, etc., is a SDVoE technology for low-latency transmission. The HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) is a transmission interface technology used for video and digital audio data sent from HDMI-compliant devices. HDBaseT is the global standard for the transmission of uncompressed ultra-high-definition audio and video, Ethernet, controls, USB and up to 100 W of power over a single cable, for up to 100 m/328 ft. Here is the overall comparison sheet of HDMI over IP vs HDBaseT differences:
| HDMI over IP | HDBaseT | |
| Cabling | HDMI cables | Ethernet cables (Cat5e or above) |
| Video signal | lossless compression | uncompressed |
| Transmission distance | unlimited | 100 m or longer with repeaters |
| Number of displays | unlimited | depending on number of ports on transmitter |
| Flexibility of device set up | flexible | relatively fixed |
| 4K capabilities | better | not so good |
| Cost | relatively higher | relatively lower |
| Future Expansion | convenient | not convenient |
A Few Points of Difference Between HDMI Over IP and HDBaseT
Here is a list of pointers that would help you understand how these technologies differ from each other. Let’s have a look at them.
Data Transmission Distance:
With HDBaseT, you can transmit HDMI signals up to 100 meters. On the other hand, HDMI over IP doesn’t have any distance limitations. As HDMI over IP is network-based, it can transmit signals over a long distance. HDMI signal distribution is achieved using several network devices, including HDMI extenders, transmitters and receivers, switches, and matrices.
Device Flexibility:
Compared to HDBaseT, HDMI over IP offers a more flexible device setup. In the HDMI over IP system, source devices are physically located in a centralized rack, rooms, or a combination of both. No matter where you locate them, they become a part of the HDMI matrix once connected to the Layer 3 managed switch. Therefore, it is possible to access them on every integrated screen using a receiver behind it. On the other hand, HDBaseT matrix switches support several remote sources on one or two inputs. The HDBaseT matrix units with this feature are expensive as more HDBaseT chipsets are required to enable this feature.
4K Capabilities:
HDMI over IP offers a better 4k experience than HDBaseT. For instance, HDMI over IP supports 4k and 1080p television on the same network. In the HDBaseT system, you need to purchase the corresponding hardware for the same functionality. It only supports one function at times, meaning either upgrade all to the 4k or reduce all TV resolutions to 1080P.
With an HDBaseT system or a fixed format matrix, distributing 4K content to a mixture of 4K and 1080p TVs involves purchasing additional signal management hardware (upping project costs), dropping the resolution of the 4K device (downing image quality), or forcing the client to replace every 1080p TV with 4K sets (upgrading functioning TVs unnessarily)!
Cost:
HDBaseT is much cheaper than HDMI over IP technology. HDBaseT- based Ethernet cables with RJ45 connectors are less expensive than HDMI cables. Against this, HDMI is a closed standard that requires a certain fee for utilizing the HDMI interface, while HDBaseT is an open standard. Therefore, it does not require any additional fees.
Future Expansion:
HDMI over IP can easily integrate new devices and provide better future expansion capabilities. For example, when using HDMI over IP, one can choose network switches with more ports than needed at present in case of additional devices are required in the future. Under such circumstances, even if the number of TVs is increased in the future, it will not affect the TVs installed already. One doesn’t need to worry that there will be no extra ports for subsequent new TVs. While HDBaseT, only supports limited devices, which is dependent on the number of transmitter ports.
Note: PoE switches are recommended (like the figure below) when choosing network switches with multiple ports in an HDMI over an IP network since there is no need to add an additional power source.
HDMI Over IP VS. HDBaseT, Which to Choose?
From all the comparisons above, it is not difficult to understand that both HDMI over IP and HDBaseT have their advantages and disadvantages when compared to each other. One should choose between them according to the real needs and budget. HDMI over IP networks can distribute high-definition video signals from one source to an unlimited number of screens/displays and offer a better 4K experience but with a higher cost. While HDBaseT could use the existing Ethernet infrastructure directly at a lower cost. Of course, one doesn’t have to just use HDBaseT or HDMI over IP because HDBaseT is fully HDMI-compliant and it works with and supports HDMI.
Conclusion
When comparing uses for HDMI vs. HDBaseT, HDMI is used primarily to connect high-definition media players, PCs, high-definition televisions, and projectors. Used primarily in enterprise networks, HDBaseT is HDMI compliant, meaning that it transmits HDMI signals - just differently than HDMI components do (using the same HDMI signal but a different wire type and modulation scheme). HDBaseT also uses a standard RJ45 connector and doesn't require specific types of legacy cables or proprietary connectors.
After understanding both technologies and their dependability on HDMI products, you must source them from a trusted industry player.